Chikungunya is an infectious disease caused by a virus. This virus is found in tropical and subtropical regions. It is transmitted by mosquitoes that bite during the day.
What are the symptoms of chikungunya?
Most people with a chikungunya infection have symptoms of illness. The acute phase of a chikungunya infection usually involves several of these symptoms in combination:
- sudden high fever
- severe joint pain, for example in fingers, wrists, ankles and elbows
- headache
- muscle pain
- back pain
- nausea
- vomiting
- skin rash (usually a few days after onset of fever)
- various eye conditions, such as conjunctivitis
Symptoms can be mild to severe. Severe symptoms are more common in people who have weaker immune symptoms, such as newborns, older people or adults who already have another health condition (comorbidities).
The acute symptoms of chikungunya usually go away within 1 to 3 weeks. Joint pain can persist for months or even years. Very few people die from chikungunya.
How does chikungunya spread?
People contract chikungunya through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes. The virus is mainly transmitted by yellow fever mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti) and Asian tiger mosquitoes (Aedes albopictus). These mosquitoes bite during the day. Besides chikungunya, they can also transmit viruses that cause other diseases, such as dengue and Zika. The time between the bite and illness is between 1 and 12 days. On average, it is 3 to 7 days.
How can I prevent chikungunya?
The main way to protect against chikungunya is by preventing mosquito bites, especially in early morning and late afternoon. That is when the Aedes mosquitoes are active. You are less likely to be infected if you wear clothes that cover your entire body and apply a mosquito repellent containing DEET to your skin. It is also advisable to sleep under a mosquito net treated with mosquito repellent, especially during the day.
Vaccine against chikungunya
In 2024, a vaccine against chikungunya for adults was authorised in Europe. As of April 2025, this vaccine is available in the Netherlands for certain travellers. Whether vaccination is recommended in your situation, for example if you are travelling to a risk area, can be discussed with the Municipal Public Health Service (GGD) or a travel health clinic.
Is there any treatment for chikungunya?
The acute symptoms of chikungunya usually go away within 1 to 3 weeks. If your joint pain continues to be severe, consult with your GP to discuss which painkillers you can use. Before using painkillers like aspirin or NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac), it is important to make sure you do not have dengue. You can use paracetamol. Sometimes physical therapy can help.
How common is chikungunya?
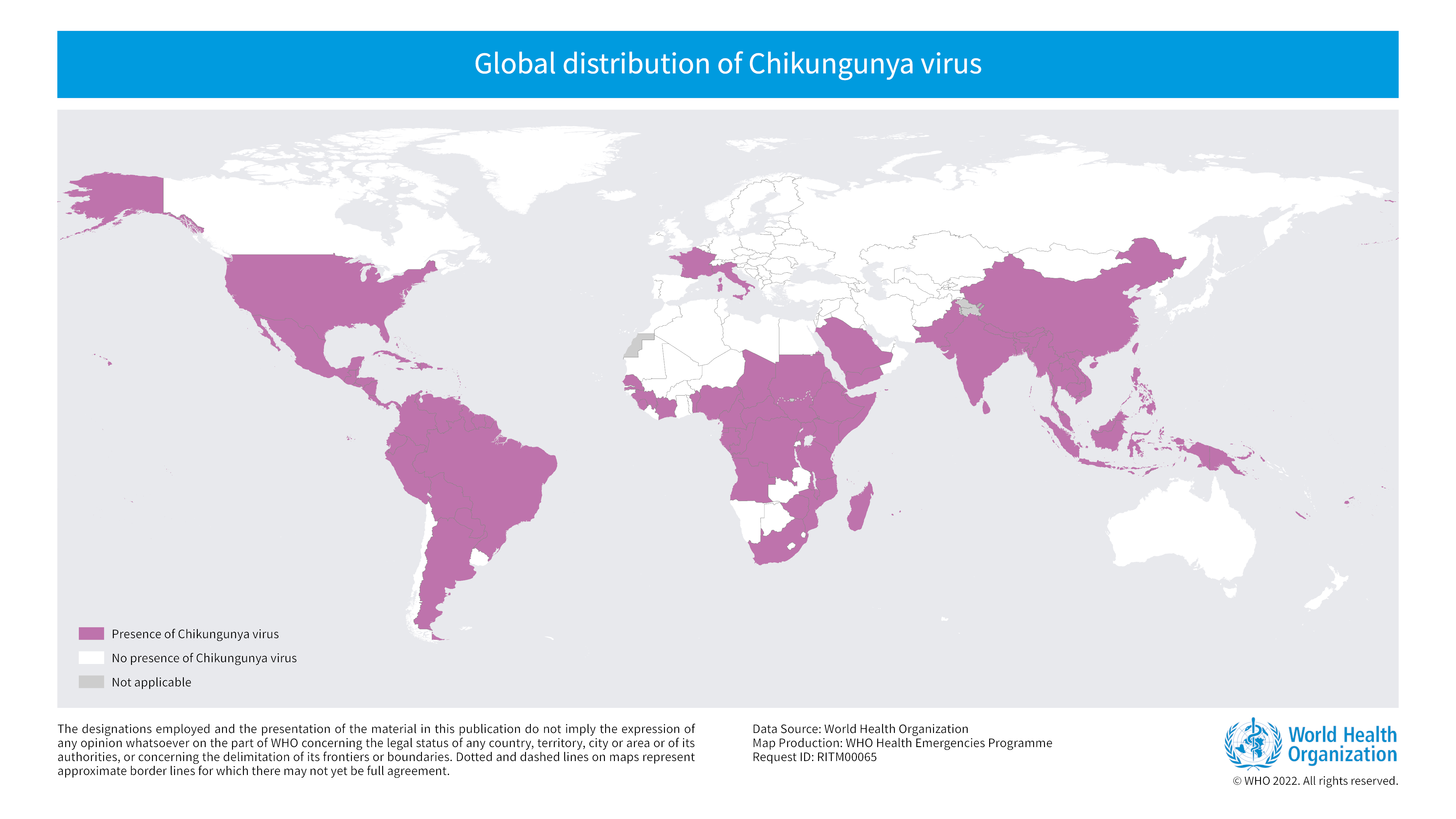
The chikungunya virus is found in Africa, Asia, Central and South America, the southern part of North America and the Caribbean. In Europe, locally transmitted cases of chikungunya have been reported in Italy (2007, 2017) and southern France (2010, 2014, 2017 and 2024).
In the European Netherlands, the only known cases of chikungunya were in people who contracted the disease in a different country. The Asian tiger mosquito is not yet common here, so it is very unlikely that anyone will contract chikungunya in the European Netherlands.
Figure: Global distribution of chikungunya virus. Credits: WHO 2022, accessed on 18 February 2025.